Over the Next Two Decades, Baby Boomers will Age in Place
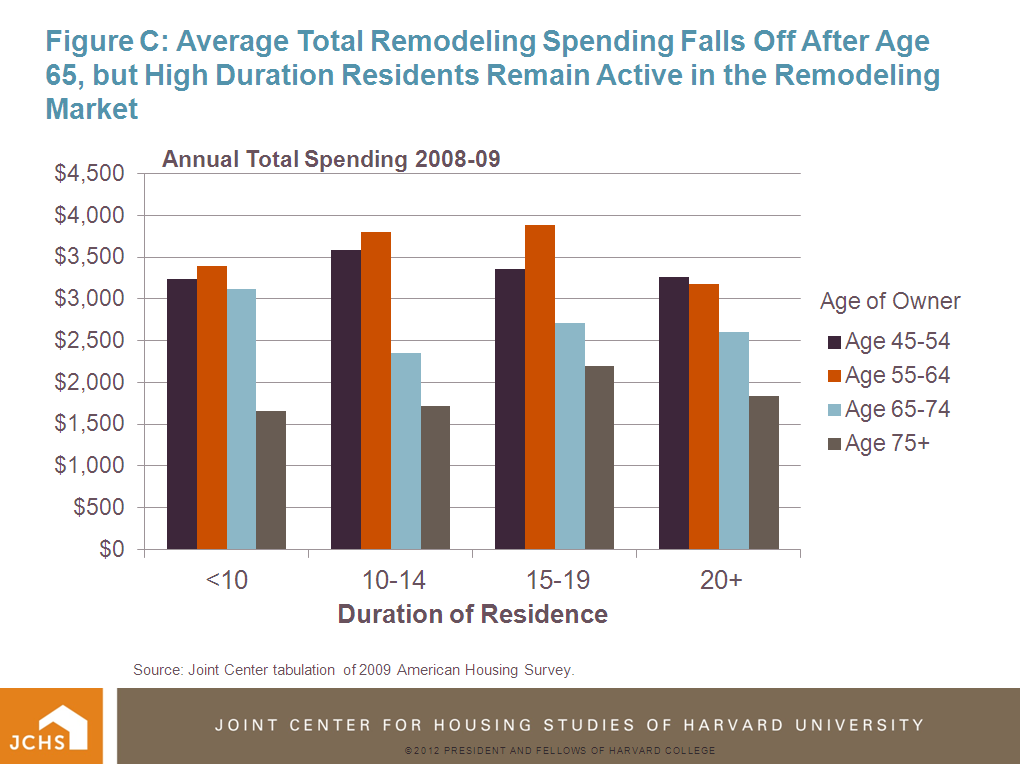
Over the next two decades, the entire baby boom generation (age 45-64 in 2010) will cross the 65+ age threshold. Baby boom homeowners have dominated housing markets for so many decades that it is easy to imagine them exercising a large influence during the next two decades as they move into their senior years. A recent report from the Bipartisan Policy Commission makes just that case, arguing that the next twenty years should see significant additions to the housing stock released by aging baby boomers because of discontinued household headship and death.
But this report fails to underscore that the vast majority of baby boom household dissolution won’t occur until after 2030. Only about 15 percent of the 46+ million units baby boomers now occupy will be turned back to the market between now and 2030, assuming cohort household dissolution rates held constant at 2000-2010 levels. This works out to about 1 million total baby boomer housing units returned to the market between 2010 and 2020, and another 6.2 million between 2020 and 2030. For owner-occupied housing, these numbers are 165,000 during 2010-2020 and 5.2 million between 2020 and 2030. If baby boomers are healthier and live longer than their immediate predecessors, these numbers should be even lower.
If more than 85 percent of baby boomers will continue to occupy housing as household heads for the next two decades, can we say anything with confidence about how they will affect housing markets? Housing analysts have mostly focused on housing adjustments that aging boomers will likely make by moving – to smaller or one-story homes (perhaps in communities that are scaled to be less automobile dependent); to retirement destinations that are warmer, have lower taxes, or are “senior oriented” in terms of services and leisure opportunities; or to locations closer to kids and grandkids. Eventually, some will find themselves moving to assisted living. While during the next two decades many boomers will do all of these things, the majority of boomers will almost certainly not do any of them. The majority of baby boom homeowners over the next two decades will simply age in place.
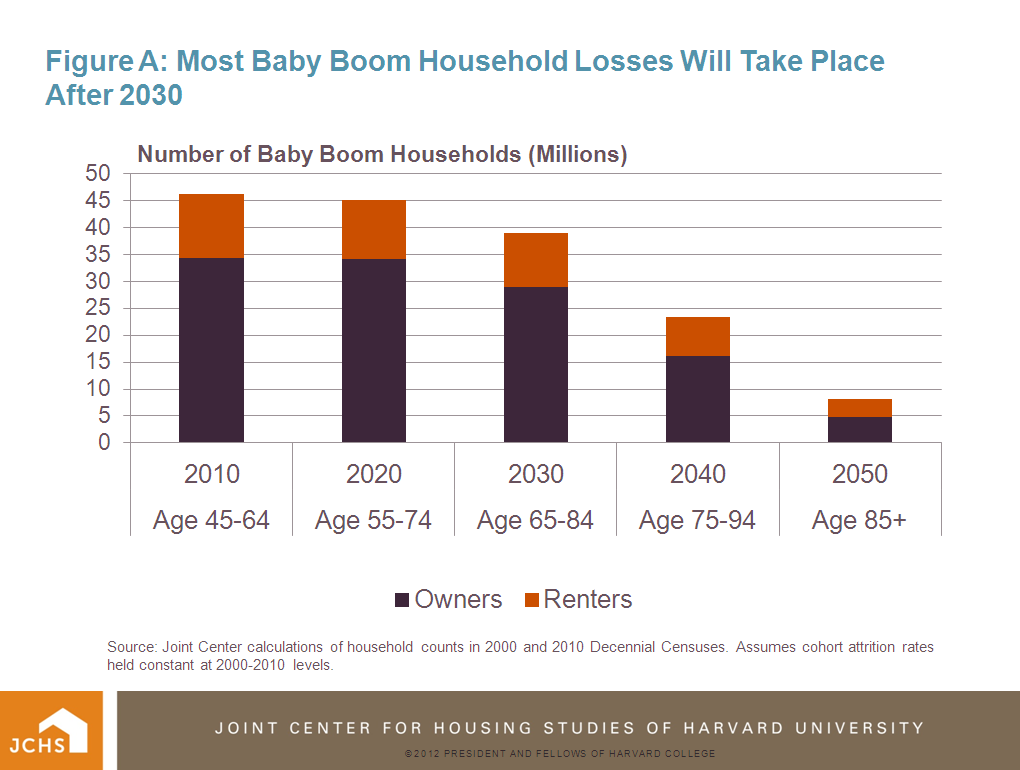
By aging in place, boomers will likely follow existing trends among older homeowners. Elderly owners are the least mobile demographic group. Less than three percent of owners age 65-74 change residences in any given year, and this fraction has been declining, while for owners age 75+, the share that moves in a given year is now about 1.5 percent. Such low mobility rates result in elderly homeowners having increasing durations of residency in their present homes: the older the owner, the higher the proportion with long-term residency. Indeed, according to the American Housing Survey, the majority of homeowners age 65+ have lived in their homes for 20 or more years (Figure B). These patterns have changed little over the past decade.
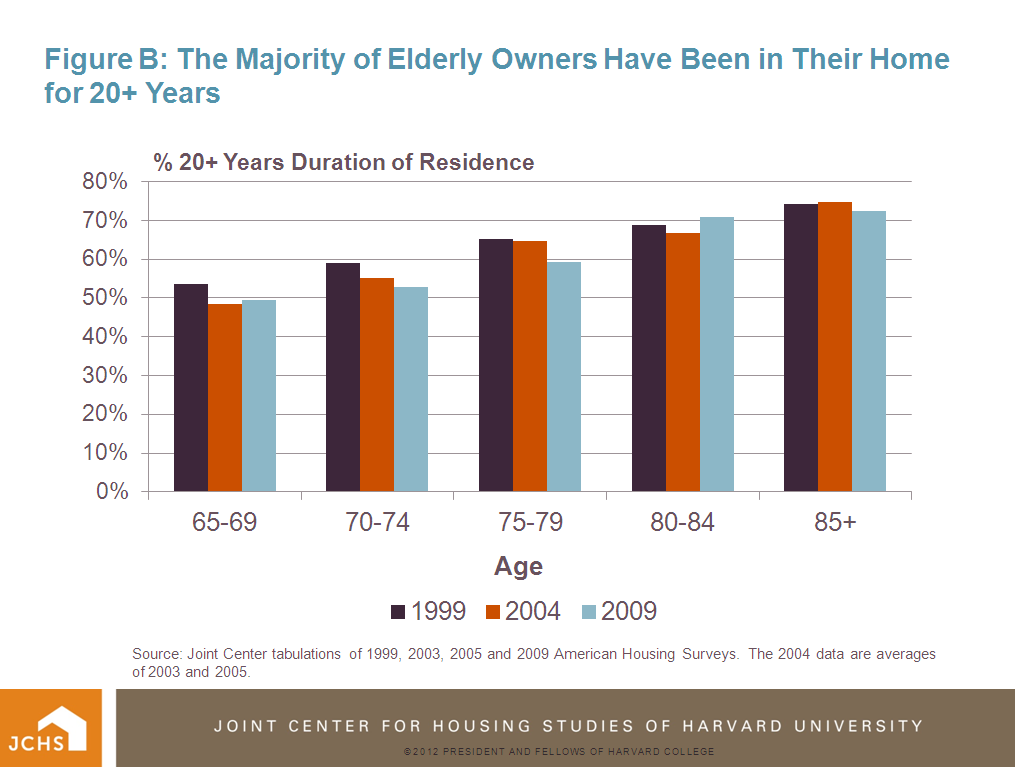
Aging in place does not necessarily mean that housing adjustments fail to take place. Renovation and remodeling activity will allow those aging in place to repair, modernize, and reconfigure their homes. Some of this remodeling activity will take place before age 65 to prepare the home for aging in place. The 50s and early 60s are an ideal time to undertake major remodeling projects – the kids have fledged the nest and the still-employed parents have some additional disposable income. Past trends suggest that while there is some fall-off in total remodeling spending after owners turn age 65, elderly owners will remain fairly active in spending on renovation and repair (Figure C). More detail about aging in place and remodeling activity is the subject of a forthcoming Joint Center working paper.